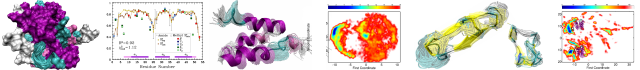Proceedings of the Natural Academy of Sciences
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences RSS feed -- current issue
URL: http://www.pnas.org
Updated: 8 years 20 weeks ago
Radially amphiphilic antimicrobial polypeptides [Chemistry]
α-Helical antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) generally have facially amphiphilic structures that may lead to undesired peptide interactions with blood proteins and self-aggregation due to exposed hydrophobic surfaces. Here we report the design of a class of cationic, helical homo-polypeptide antimicrobials with a hydrophobic internal helical core and a charged exterior shell,...
Categories: Journal Articles
A complexity classification of spin systems [Computer Sciences]
We study the computational complexity of approximating the partition function of a q-state spin system with an external field. There are just three possible levels of computational difficulty, depending on the interaction strengths between adjacent spins: (i) efficiently exactly computable, (ii) equivalent to the ferromagnetic Ising model, and (iii) equivalent...
Categories: Journal Articles
Dishevelled downregulates Wnt signaling [Developmental Biology]
Wnt proteins regulate axonal outgrowth along the anterior–posterior axis, but the intracellular mechanisms that modulate the strength of Wnt signaling in axon guidance are largely unknown. Using the Caenorhabditis elegans mechanosensory PLM neurons, we found that posteriorly enriched LIN-44/Wnt acts as a repellent to promote anteriorly directed neurite outgrowth through...
Categories: Journal Articles
Lgr6 is required for digit tip regeneration [Developmental Biology]
The tips of the digits of some mammals, including human infants and mice, are capable of complete regeneration after injury. This process is reliant on the presence of the overlaying nail organ and is mediated by a proliferative blastema. Epithelial Wnt/β-catenin signaling has been shown to be necessary for mouse...
Categories: Journal Articles
NF-{kappa}B and heart regeneration [Developmental Biology]
Heart regeneration offers a novel therapeutic strategy for heart failure. Unlike mammals, lower vertebrates such as zebrafish mount a strong regenerative response following cardiac injury. Heart regeneration in zebrafish occurs by cardiomyocyte proliferation and reactivation of a cardiac developmental program, as evidenced by induction of gata4 regulatory sequences in regenerating...
Categories: Journal Articles
Masked CO2 forcing directly slows tropical winds [Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences]
Climate models robustly simulate weakened mean circulations of the tropical atmosphere in direct response to increased carbon dioxide (CO2). The direct response to CO2, defined by the response to radiative forcing in the absence of changes in sea surface temperature, affects tropical precipitation and tropical cyclone genesis, and these changes...
Categories: Journal Articles
Amazon extreme weather events [Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences]
Future intensification of Amazon drought resulting from climate change may cause increased fire activity, tree mortality, and emissions of carbon to the atmosphere across large areas of Amazonia. To provide a basis for addressing these issues, we examine properties of recent and future meteorological droughts in the Amazon in 35...
Categories: Journal Articles
Migration of the Asian monsoon in a warmer world [Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences]
Glacial–interglacial changes in the distribution of C3/C4 vegetation on the Chinese Loess Plateau have been related to East Asian summer monsoon intensity and position, and could provide insights into future changes caused by global warming. Here, we present δ13C records of bulk organic matter since the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM)...
Categories: Journal Articles
Exceptionally large wildfire outbreaks in the MCA [Ecology]
Many of the largest wildfires in US history burned in recent decades, and climate change explains much of the increase in area burned. The frequency of extreme wildfire weather will increase with continued warming, but many uncertainties still exist about future fire regimes, including how the risk of large fires...
Categories: Journal Articles
Lianas reduce carbon accumulation and storage [Ecology]
Tropical forests store vast quantities of carbon, account for one-third of the carbon fixed by photosynthesis, and are a major sink in the global carbon cycle. Recent evidence suggests that competition between lianas (woody vines) and trees may reduce forest-wide carbon uptake; however, estimates of the impact of lianas on...
Categories: Journal Articles
Elevated CO2 modifies ocean ecosystem functioning [Ecology]
Rising anthropogenic CO2 emissions are anticipated to drive change to ocean ecosystems, but a conceptualization of biological change derived from quantitative analyses is lacking. Derived from multiple ecosystems and latitudes, our metaanalysis of 632 published experiments quantified the direction and magnitude of ecological change resulting from ocean acidification and warming...
Categories: Journal Articles
Microbial firewall against euxinia [Ecology]
Seasonal oxygen depletion (hypoxia) in coastal bottom waters can lead to the release and persistence of free sulfide (euxinia), which is highly detrimental to marine life. Although coastal hypoxia is relatively common, reports of euxinia are less frequent, which suggests that certain environmental controls can delay the onset of euxinia....
Categories: Journal Articles
Surface ops can affect Marcellus groundwater [Environmental Sciences]
Hundreds of organic chemicals are used during natural gas extraction via high-volume hydraulic fracturing (HVHF). However, it is unclear whether these chemicals, injected into deep shale horizons, reach shallow groundwater aquifers and affect local water quality, either from those deep HVHF injection sites or from the surface or shallow subsurface....
Categories: Journal Articles
Complex constraints on allometry [Evolution]
Precise exponential scaling with size is a fundamental aspect of phenotypic variation. These allometric power laws are often invariant across taxa and have long been hypothesized to reflect developmental constraints. Here we test this hypothesis by investigating the evolutionary potential of an allometric scaling relationship in drosophilid wing shape that...
Categories: Journal Articles
Coevolution of virulence and mating strategies [Evolution]
Parasites are thought to play an important role in sexual selection and the evolution of mating strategies, which in turn are likely to be critical to the transmission and therefore the evolution of parasites. Despite this clear interdependence we have little understanding of parasite-mediated sexual selection in the context of...
Categories: Journal Articles
Habitat alters route and pace of human dispersals [Evolution]
Unlike most other biological species, humans can use cultural innovations to occupy a range of environments, raising the intriguing question of whether human migrations move relatively independently of habitat or show preferences for familiar ones. The Bantu expansion that swept out of West Central Africa beginning ∼5,000 y ago is...
Categories: Journal Articles
River shark evolution [Evolution]
For over a hundred years, the “river sharks” of the genus Glyphis were only known from the type specimens of species that had been collected in the 19th century. They were widely considered extinct until populations of Glyphis-like sharks were rediscovered in remote regions of Borneo and Northern Australia at...
Categories: Journal Articles
Genetics of biopsy-derived tumor organoids [Genetics]
Tumor organoids are 3D cultures of cancer cells. They can be derived from the tumor of each individual patient, thereby providing an attractive ex vivo assay to tailor treatment. Using patient-derived tumor organoids for this purpose requires that organoids derived from biopsies maintain the genetic diversity of the in vivo...
Categories: Journal Articles
HLA-G cycle [Immunology and Inflammation]
The interaction of noncytotoxic decidual natural killer cells (dNK) and extravillous trophoblasts (EVT) at the maternal–fetal interface was studied. Confocal microscopy revealed that many dNK interact with a single large EVT. Filamentous projections from EVT enriched in HLA-G were shown to contact dNK, and may represent the initial stage of...
Categories: Journal Articles
Modified peptides create super agonists in T1D [Immunology and Inflammation]
Chromogranin A (ChgA) is an autoantigen for CD4+ T cells in the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse model of type 1 diabetes (T1D). The natural ChgA-processed peptide, WE14, is a weak agonist for the prototypical T cell, BDC-2.5, and other ChgA-specific T-cell clones. Mimotope peptides with much higher activity share a...
Categories: Journal Articles