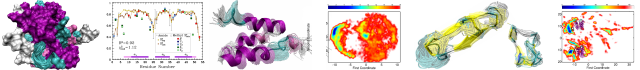Journal Articles
Mapping the Protein Fold Universe Using the CamTube Force Field in Molecular Dynamics Simulations
by Predrag Kukic, Arvind Kannan, Maurits J. J. Dijkstra, Sanne Abeln, Carlo Camilloni, Michele Vendruscolo
It has been recently shown that the coarse-graining of the structures of polypeptide chains as self-avoiding tubes can provide an effective representation of the conformational space of proteins. In order to fully exploit the opportunities offered by such a ‘tube model’ approach, we present here a strategy to combine it with molecular dynamics simulations. This strategy is based on the incorporation of the ‘CamTube’ force field into the Gromacs molecular dynamics package. By considering the case of a 60-residue polyvaline chain, we show that CamTube molecular dynamics simulations can comprehensively explore the conformational space of proteins. We obtain this result by a 20 μs metadynamics simulation of the polyvaline chain that recapitulates the currently known protein fold universe. We further show that, if residue-specific interaction potentials are added to the CamTube force field, it is possible to fold a protein into a topology close to that of its native state. These results illustrate how the CamTube force field can be used to explore efficiently the universe of protein folds with good accuracy and very limited computational cost.
Categories: Journal Articles
Efficient Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation at Neutral and High pH by Adventitious Nickel at Nanomolar Concentrations
Categories: Journal Articles
Topological framework for local structure analysis [Applied Physical Sciences]
Physical systems are frequently modeled as sets of points in space, each representing the position of an atom, molecule, or mesoscale particle. As many properties of such systems depend on the underlying ordering of their constituent particles, understanding that structure is a primary objective of condensed matter research. Although perfect...
Categories: Journal Articles
Abrupt shifts in IPCC climate models [Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences]
Abrupt transitions of regional climate in response to the gradual rise in atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations are notoriously difficult to foresee. However, such events could be particularly challenging in view of the capacity required for society and ecosystems to adapt to them. We present, to our knowledge, the first systematic...
Categories: Journal Articles
Structure of nucleosomal barrier for transcription [Biochemistry]
Thousands of human and Drosophila genes are regulated at the level of transcript elongation and nucleosomes are likely targets for this regulation. However, the molecular mechanisms of formation of the nucleosomal barrier to transcribing RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and nucleosome survival during/after transcription remain unknown. Here we show that...
Categories: Journal Articles
Temporal evolution of helix hydration in ChR2 [Biophysics and Computational Biology]
The discovery of channelrhodopsins introduced a new class of light-gated ion channels, which when genetically encoded in host cells resulted in the development of optogenetics. Channelrhodopsin-2 from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, CrChR2, is the most widely used optogenetic tool in neuroscience. To explore the connection between the gating mechanism and the influx...
Categories: Journal Articles
Species specificity of a ribosome from a pathogen [Biophysics and Computational Biology]
The emergence of bacterial multidrug resistance to antibiotics threatens to cause regression to the preantibiotic era. Here we present the crystal structure of the large ribosomal subunit from Staphylococcus aureus, a versatile Gram-positive aggressive pathogen, and its complexes with the known antibiotics linezolid and telithromycin, as well as with a...
Categories: Journal Articles
CD31 antagonizes extrinsic proapoptotic signals [Immunology and Inflammation]
Constitutive resistance to cell death induced by inflammatory stimuli activating the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis is a key feature of vascular endothelial cells (ECs). Although this property is central to the maintenance of the endothelial barrier during inflammation, the molecular mechanisms of EC protection from cell-extrinsic, proapoptotic stimuli have not...
Categories: Journal Articles
I{kappa}B{zeta} plays an important role in psoriasis [Immunology and Inflammation]
Psoriasis is a common immune-mediated, chronic, inflammatory skin disease characterized by hyperproliferation and abnormal differentiation of keratinocytes and infiltration of inflammatory cells. Although TNFα- and IL-17A–targeting drugs have recently proven to be highly effective, the molecular mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of psoriasis remains poorly understood. We found that expression of...
Categories: Journal Articles
Mycobacterial {alpha}-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase [Microbiology]
Enzymes of central carbon metabolism (CCM) in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) make an important contribution to the pathogen’s virulence. Evidence is emerging that some of these enzymes are not simply playing the metabolic roles for which they are annotated, but can protect the pathogen via additional functions. Here, we found that...
Categories: Journal Articles
Gene therapy at late-stage retinal degeneration [Neuroscience]
Inherited retinal degenerations cause progressive loss of photoreceptor neurons with eventual blindness. Corrective or neuroprotective gene therapies under development could be delivered at a predegeneration stage to prevent the onset of disease, as well as at intermediate-degeneration stages to slow the rate of progression. Most preclinical gene therapy successes to...
Categories: Journal Articles
Mushroom bodies enable complex learning in bees [Neuroscience]
Learning theories distinguish elemental from configural learning based on their different complexity. Although the former relies on simple and unambiguous links between the learned events, the latter deals with ambiguous discriminations in which conjunctive representations of events are learned as being different from their elements. In mammals, configural learning is...
Categories: Journal Articles
Postsymptomatic ASOs in spinal muscular atrophy [Neuroscience]
Clinical presentation of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) ranges from a neonatal-onset, very severe disease to an adult-onset, milder form. SMA is caused by the mutation of the Survival Motor Neuron 1 (SMN1) gene, and prognosis inversely correlates with the number of copies of the SMN2 gene, a human-specific homolog of...
Categories: Journal Articles
Mouse odorant receptor-specific glomeruli [Neuroscience]
In the mouse, axons of olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) that express the same odorant receptor (OR) gene coalesce into one or a few glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. The positions of OR-specific glomeruli are traditionally described as stereotyped. Here, we have assessed quantitatively the positions of OR-specific glomeruli using serial...
Categories: Journal Articles
PAK3 regulates AMPAR trafficking [Neuroscience]
AMPA receptors (AMPARs) are the major excitatory receptors of the brain and are fundamental to synaptic plasticity, memory, and cognition. Dynamic recycling of AMPARs in neurons is regulated through several types of posttranslational modification, including phosphorylation. Here, we identify a previously unidentified signal transduction cascade that modulates phosphorylation of serine...
Categories: Journal Articles
Resonance as a mechanism for elastic limb behavior [Physiology]
In terrestrial locomotion, there is a missing link between observed spring-like limb mechanics and the physiological systems driving their emergence. Previous modeling and experimental studies of bouncing gait (e.g., walking, running, hopping) identified muscle-tendon interactions that cycle large amounts of energy in series tendon as a source of elastic limb...
Categories: Journal Articles
Correction for Lee et al., Development of a histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor and its biological effects [Correction]
CHEMISTRY, BIOCHEMISTRY Correction for “Development of a histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor and its biological effects,” by Ju-Hee Lee, Yuanshan Yao, Adaickapillai Mahendran, Lang Ngo, Gisela Venta-Perez, Megan L. Choy, Ronald Breslow, and Paul A. Marks, which appeared in issue 39, September 29, 2015, of Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (112:12005–12010;...
Categories: Journal Articles
Correction for Lee et al., RNA design rules from a massive open laboratory [Correction]
BIOCHEMISTRY Correction for “RNA design rules from a massive open laboratory,” by Jeehyung Lee, Wipapat Kladwang, Minjae Lee, Daniel Cantu, Martin Azizyan, Hanjoo Kim, Alex Limpaecher, Sungroh Yoon, Adrien Treuille, Rhiju Das, and EteRNA Participants, which appeared in issue 6, February 11, 2014, of Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (111:2122–2127;...
Categories: Journal Articles
Correction for Lin et al., Induction of USP25 by viral infection promotes innate antiviral responses by mediating the stabilization of TRAF3 and TRAF6 [Correction]
IMMUNOLOGY AND INFLAMMATION Correction for “Induction of USP25 by viral infection promotes innate antiviral responses by mediating the stabilization of TRAF3 and TRAF6,” by Dandan Lin, Man Zhang, Meng-Xin Zhang, Yujie Ren, Quanyi Zhao, Jie Jin, Zishu Pan, Min Wu, Hong-Bing Shu, Chen Dong, and Bo Zhong, which appeared in...
Categories: Journal Articles
Correction for Lu et al., Label-free DNA imaging in vivo with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy [Correction]
MEDICAL SCIENCES, APPLIED PHYSICAL SCIENCES Correction for “Label-free DNA imaging in vivo with stimulated Raman scattering microscopy,” by Fa-Ke Lu, Srinjan Basu, Vivien Igras, Mai P. Hoang, Minbiao Ji, Dan Fu, Gary R. Holtom, Victor A. Neel, Christian W. Freudiger, David E. Fisher, and X. Sunney Xie, which appeared in...
Categories: Journal Articles